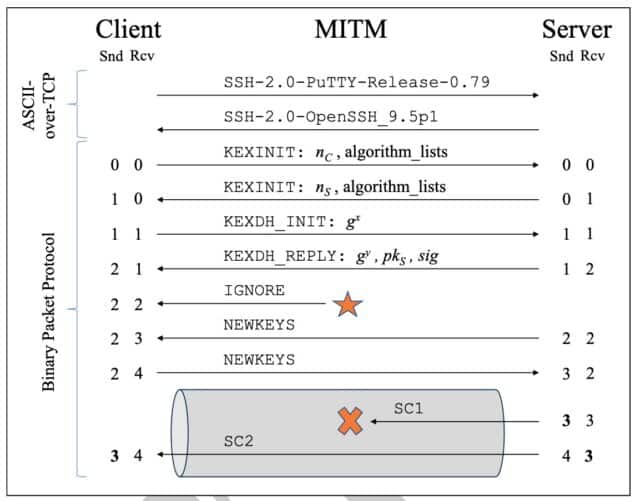
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the emergence of the Terrapin attack has presented a new and significant challenge. This novel cryptographic attack specifically targets the integrity of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, a cornerstone of secure communication in networks. The Terrapin attack, exploiting weaknesses in widely used algorithms like ChaCha20-Poly1305 and CBC-EtM, can strip away the protected messages at the start of a secure channel, leading to a breakdown in integrity. Such vulnerabilities can compromise the negotiation of security-relevant protocol extensions and, in some cases, result in a total loss of confidentiality and integrity.
This is where microsegmentation, particularly platforms like Enclave, emerges as a critical line of defense. Microsegmentation is a security concept that involves dividing a network into distinct segments, where each segment contains network entities with similar security requirements. By implementing microsegmentation, organizations can significantly reduce the attack surface and contain breaches more effectively.
Enclave’s Approach to Microsegmentation
Enclave is a state-of-the-art micro-segmentation tool that leverages overlay networks, firewalls, and a Zero Trust network permissions model to create secure, access-controlled spaces, or enclaves. These enclaves are fortified segments where access is strictly limited to specified machines and users.
- Secure Communication: Enclave employs firewall rules and encryption to protect communication between nodes. This layer of security is vital in preventing attacks like Terrapin, which target the integrity of data transmission.
- Enclave Management Console (EMC): As the central control system, the EMC allows for comprehensive configuration of microsegments, authentication management, and network settings alterations. This centralized management ensures consistent security policies across all network segments.
- Agents and Beacons: Enclave utilizes two types of agents – user and node agents. User agents are temporary, ideal for tasks similar to VPN access, while node agents are meant for permanent connections, like a web server to a database. Beacons in Enclave provide resolution functions, translating overlay IP space to physical IP space, much like DNS systems. This setup is critical in maintaining the integrity of the network against sophisticated attacks.
Why Microsegmentation is Vital Against Terrapin Attack
- Reduced Attack Surface: By segmenting the network, microsegmentation limits the potential points of entry for attackers, directly countering the Terrapin attack’s ability to exploit SSH vulnerabilities.
- Containment of Breaches: Enclave’s microsegmentation strategy significantly reduces the time it takes to identify and contain breaches. In 2021, the average lifecycle of a breach was 286 days from identification to containment. Enclave can drastically reduce this time, limiting the scope and impact of an attack.
- Immobilization of Insider Threats: Enclave’s approach ensures that even if an attacker gains access to the network, they cannot freely move laterally across the network. This is crucial in defending against attacks like Terrapin that could potentially exploit internal vulnerabilities.
As the Terrapin attack illustrates a new frontier in cybersecurity threats, the implementation of microsegmentation strategies, particularly those offered by platforms like Enclave, becomes not just beneficial but essential. These strategies provide a robust defense mechanism, safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of network communications against sophisticated cyber attacks.